

An adult male Aotus nancymae (No. 15) was wildcaught in Cocha Zapote in the Amazon river basin [1] on February 4, 1979. After quarantine, it was introduced into the Aotus colony at the Center for Reproduction and Conservation of Non-Human Primates in Iquitos, Peru, and paired with a wildcaught adult female (No. 14) under previously described conditions [4]. They were maintained in the colony without signs of reproductive activity until April 17, 1982, when the female was removed for research purposes and the male was paired with another wildcaught adult female (No. 20) on June 14, 1982. A birth was observed on November 15, 1986. The newborn, a female, was identified as T-81. On May 21, 1987, the female (No. 20) died unexpectedly. On June 19, 1987, the male's left testicle was observed to be swollen, the animal was treated with Tetracycline (Emicina, Pfizer Corp. Farm., Ap. 2917 Lima 100, PERU), and the monkey apparently improved. Nine months later, on March 8, 1988, the same testicle was observed swollen. The same treatment was institued, but the animal did not improve. On May 9, 1988, the testicle was removed surgically by one of the authors (T.N.). Tissue samples were fixed in 10% formalin and processed routinely for hematoxylin and eosin staining. After an uneventful recovery, the monkey was returned to its cage in the colony and on December 9, 1988, it was paired with a captive-born adult female (T-87). At present, two offsprings have been obtained: the male T-244 born on September 11, 1989, and the female T-337 bom on October 26, 1990.
Pathology
The surgically removed mass, measuring 3 X 2 X 2 cm approximately, was about two to three times the size of a normal adult owl monkey testicle. Grossly, on cut surface, the mass was soft, white to pale gray with focal clear and darker areas, and bulged above the adjacent tissue. Apparently, no metastasis was observed in adjacent tissues and spermatic cord.
 |
 |
||
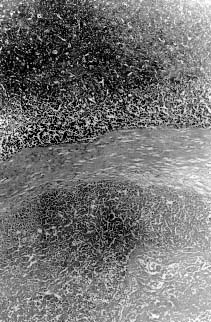
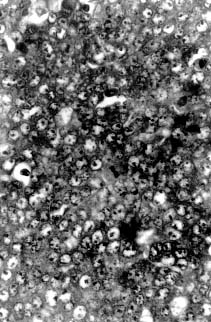
| Fig. 1. Large areas of necrosis scattered throughout the tumor forming lobules surrounded by well-defined fibrous strands. 62.5 x, H&E. | Fig. 2. Mitotic figures observed at high power field. 500 x H&E. |
Microscopically, the mass was composed of closely packed ribbons and nests of large round to polygonal cells with low amounts of basophilic cytoplasm and large round nuclei with prominent nucleoli divided into demarcated lobules by delicate septa of fibrous tissue. Large areas of necrosis werescattered throughout the mass forming lobules surrounded by well-defined fibrous strands (Fig. 2). The morphology of the tumor cells was consistent with a seminoma. In addition, clusters of small round to oval eosinophilic cells with condensed round nuclei were observed occasionally in the middle of some lobules. A minimum amount of hemorrhage was also observed.
